
Quick Action Can Affect Impact of Stroke
A stroke can happen very suddenly to anyone at any time… and without much warning. Most of us know at least someone close to us who has had a stroke, and some of us know multiple victims of stroke. Many individuals who experience a stroke recover fully. Some are left disabled in some way. Sadly, others pass away.
The unfortunate truth is that more people have experienced – or will experience – a stroke than the general public may realize. As common as strokes are and as often as we hear about them, too few people understand what a stroke is, how to identify when someone is having a stroke, or what to do in the situation. This important information can help save lives and reduce the impact of the stroke.
In very basic and non-medical terms, most strokes happen when the brain is damaged because the flow of blood has been suddenly cut off from one or more areas in the brain. The body depends upon an adequate amount of blood reaching the brain in order for the brain and nervous system to function properly. Without enough oxygen, cells in the brain begin dying very quickly. As a result, other parts of the body controlled by the damaged areas of the brain stop working as they should.
The most common symptoms of a stroke include facial weakness, arm weakness, and difficulty speaking. However, there are many other signs to look for that may mean someone could be having a stroke. (See our list of symptoms below) In some instances, a person having a stroke may exhibit only one symptom. In other cases, a person may experience a combination of symptoms. Stroke symptoms may be last only a few minutes and vanish almost immediately or they may continue for hours. They may be mildly uncomfortable or they may cause extreme distress.
It isn’t all that unusual for someone to have a mild or a “mini” stroke without ever realizing it, especially if symptoms are fleeting. A mild stroke is often referred to by medical professionals as a transient ischemic attack or TIA. It can be very easy to ignore the seemingly minor symptoms of a mild stroke or to chalk them up to some other cause. But, even if symptoms do not seem serious or disappear quickly, they should NEVER be ignored.
The severity and outcome of a stroke depends on where the brain is damaged, how much of the brain is damaged, and how long it takes to restore blood supply to the damaged areas of the brain. The longer a stroke continues without medical treatment, the more damage may be done. A severe stroke can be permanently debilitating or lead to death.
Taking the right action quickly can help keep the extent of brain damage to a minimum, increase survival odds, and improve the extent of recovery that will be possible for the person following the stroke. What is the right action? Whenever a stroke might be a possibility, calling 911 is imperative. It is also vital to make sure to be specific with the 911 operator about your suspicion that someone might be having a stroke.
Fast action increases the chance for effective treatment. Some stroke treatments/medications must be administered within hours of the start of stroke symptoms. So, the sooner a stroke victim gets to the hospital, the better. An emergency medical care team responding to a 911 call is able to quickly determine if their patient is having a stroke. They will then provide appropriate medical aid right away and alert hospital staff that a stroke patient is on route to the facility. Preparations can then be made at the hospital in advance and treatment can begin immediately when the patient arrives.
Speak with your doctor about your personal risk for stroke. He or she will be able to help you take steps necessary to prepare and protect yourself.
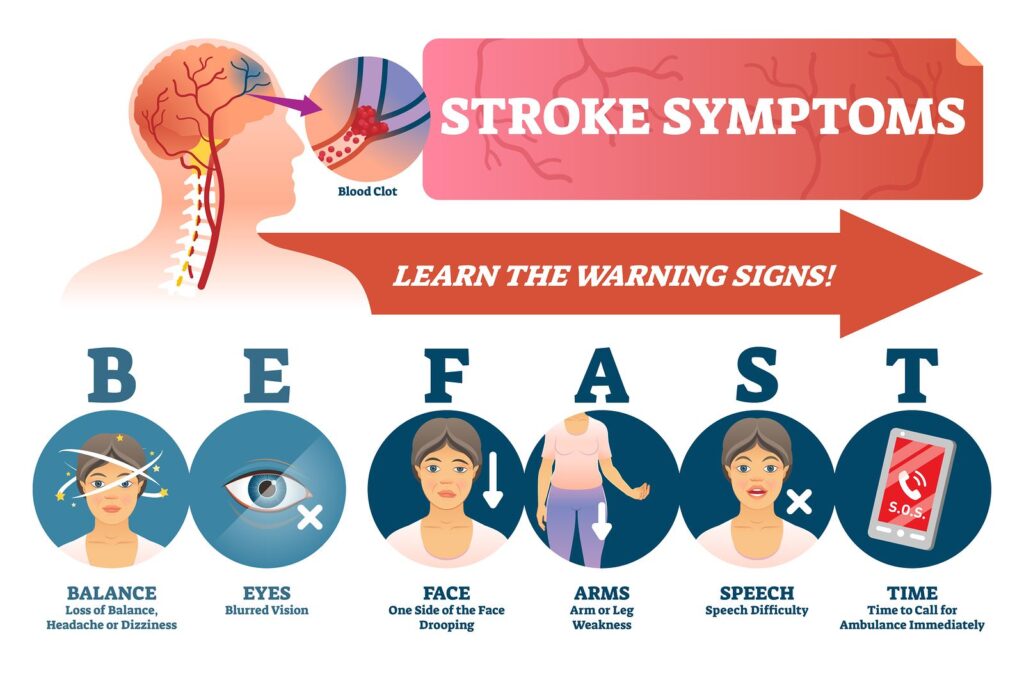
BE FAST
The “BE FAST” assessment test is a simple, straightforward method to help us recognize the most common signs of stroke and act accordingly.
B – Sudden loss of BALANCE
E – Sudden loss of vision in one or both EYES
F – FACIAL drooping or numbness
A – ARM weakness or numbness
S – Difficulty SPEAKING
T – TIME to call 911 if someone shows any of these symptoms, even if the symptoms go away.
Common Stroke Symptoms
The following are just some of the more common symptoms that may signal a stroke. Some are symptoms of other health issues as well. It is important to seek medical attention to know for sure what may be causing any questionable health concern. Do not wait.
- Weakness or paralysis in the face
- Weakness or paralysis in an arm or leg
- Weakness or paralysis in one side of the body
- Problems speaking and/or swallowing
- Loss of vision or changed vision in one or both eyes
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Lack of sensation

Age Adds Flavor
We are not old, we are seasoned!
Don’t forget to visit us on FACEBOOK!
